SEO Basics: How to Do SEO for Beginners

This is a complete SEO guide for beginners.
This new guide will cover all of the SEO basics you need to know.
(Along with plenty of actionable tips, strategies, and tactics that you can implement right away.)
So if you want to rank your website higher in Google search, this SEO beginner’s guide is for you.
What Is SEO?
SEO is the process of improving the performance and experience of your website so it can gain better visibility in search engines.
Specifically, SEO is all about ranking in the organic search results.
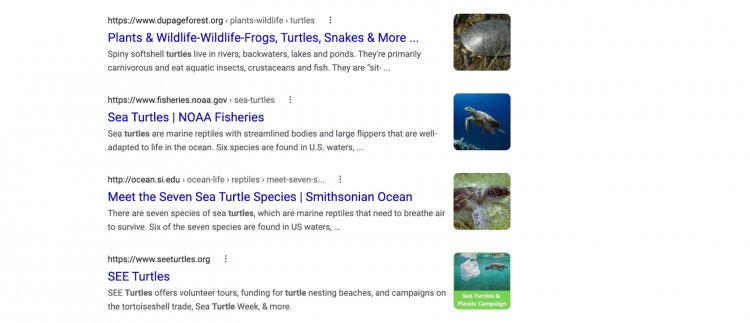
You see, Google’s search results are split up into two sections: ads and organic results.
Ads (as the name suggests) are results that people pay for via Google Ads. This is a completely separate system from the organic results.
The organic results are based 100% on quality. And are not “pay to play.”
It’s the organic results where SEO becomes important.
Why Is SEO Important?
SEO is a great way to bring more traffic, leads, customers, and revenue to your business.
In fact, 81% of all Google searchers click on the organic results.
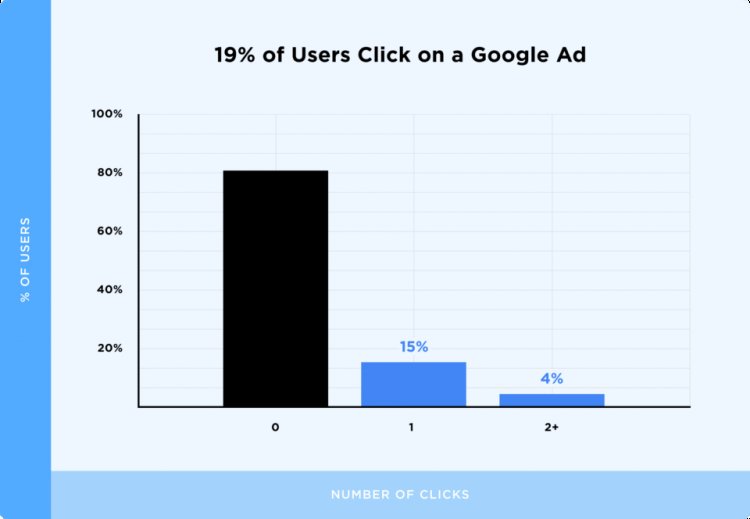
Which means only 19% choose to click on an ad.
Put another way: you can expect around 5x more traffic by ranking in the organic search results vs. paying for an ad.
(Even though ads are at the top of the page.)
And when SEO is done right, the results can add up fast.
For example, Amazon gets over 386 million organic visitors per month from Google:
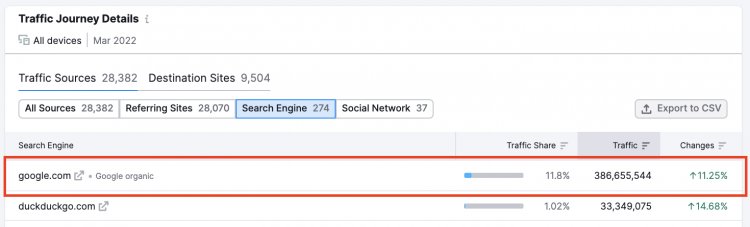
Not bad. But it gets better.
If you add up how much it would cost Amazon to get the same traffic via Google Ads (known as “Traffic cost”), that comes to $1.8M/month.
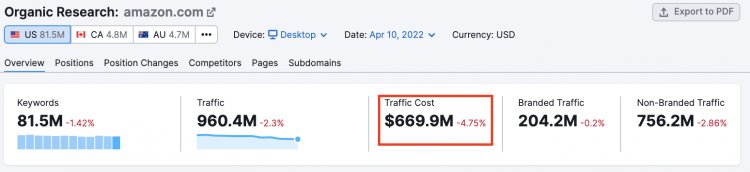
And unlike paid traffic, these organic visitors come in whether or not Amazon is actively running ads.
To be clear: SEO is an ongoing process that takes work. But once you rank for a set of keywords, your rankings typically remain stable over time.
In short, the main benefits of SEO include:
- Ensure that your brand is visible when your potential customers search on Google
- Drive targeted traffic to your website from people interested in your product or service
- Result in increased organic revenue
- Give you a solid competitive advantage
SEO Basics (Things to Do Right Now)
Before we get into the specific steps you need to take to rank higher in Google, let’s get some basic SEO steps out of the way.
These steps will ensure that Google can properly crawl and index your site. And that the following strategies will work for you.
First, check to see if your site is already indexed in Google.
Specifically, do a “site:yoursite.com” search on Google.
It will show you whether or not Google has already crawled and indexed your site. And if so, around how many pages they’ve indexed so far.
If your site shows up in the results, great! You’re all set.
If not, it could just mean that your site is new. And Google hasn’t found it yet.
It could also mean that your site has inadvertently blocked search engines from crawling it (which is surprisingly common!) Either way, you want to get this fixed ASAP.
This guide to fixing crawlability issues will help you figure out what’s wrong. And get it fixed.
Second, connect your website with Google Search Console.
Search Console is a free tool from Google that serves as sort of a liaison between you and Big G.

Specifically, it lets you know things like:
- How often your site appears in search
- Which keywords you rank for
- How many pages from your site Google has indexed
- Issues crawling, indexing, or rendering your pages
So yeah, if you want to succeed with SEO, Google Search Console is kind of a big deal.
This guide will walk you through how to use it.
Finally, create and submit a sitemap.
A sitemap is just like it sounds: a “map” of your site.

Google and other search engines use sitemaps to find all of the pages on your site.
Which helps ensure that they’re crawling and indexing all of your important pages.
How you exactly create a sitemap depends on what your site runs on (WordPress, Shopify, etc.)
Either way, it’s worth creating an XML sitemap.
And submitting that sitemap to Google via the Search Console.

Once those SEO basics are complete, it’s time to get into the meat of this SEO beginner’s guide.
Starting with one of the more critical elements of SEO: keyword research.
Keyword Research
Learning the SEO basics means getting a solid grasp of how to do keyword research the right way. Let’s see exactly how.
1. Find Your Site’s Primary Keywords
Often referred to as “money” keywords, primary keywords are terms that customers search for when they’re searching for exactly what you sell.
For example, for an SEO software company, some primary keywords might include:
- SEO software
- SEO tools
- Keyword research tool
- Rank tracking
Thing is, primary keywords are usually competitive.
Which means it will take a new site time to be able to rank for these terms.
So you want to consider these your long-term targets in your SEO strategy.
Here’s how to find your site’s primary keywords:
First, jot down the different terms that you’d expect a customer or client to use when looking for a business like yours on Google.
For example, let’s say you run an ecommerce website that sells natural dog food.
Primary keywords for your site would be things like:
- Organic dog food
- Natural dog food
- Buy dog food online
- Healthy dog food
There are no right or wrong terms here. This is really more of a brainstorming approach. The goal is to list as many relevant keywords as possible.
Once you have a list of potential keywords, head over to the keyword research tool of your choosing.
For this example, we’ll use our Keyword Overview tool.
Enter the search terms from your list and select “Analyze.”

The tool returns a list of metrics for each keyword, including their monthly search volume and keyword difficulty (KD).
These are two key stats here to take note of that you’ll use to choose the best primary keywords from your list.

Monthly search volume is just like it sounds: the number of searches that keyword gets every month on Google.
Obviously, the higher the search volume, the more potential traffic you can get.
The flip side is that higher search volume also means more keyword difficulty (KD % in Semrush).
Keyword difficulty is essentially how difficult it will be to rank on the first page of Google for that term. Needless to say, the lower this is, the better.
2. Find Long Tail Keywords and Keyword Variations
The list of primary keywords you just came up with may be good to go. However, it’s worth generating long-tail visions of those terms as well.
Long-tail keywords are longer search terms that typically have a lower search volume but a higher level of intent.

Which means they can convert at a higher percentage compared to primary keywords. Plus, they tend to have lower levels of first-page competition. A win-win!
The Keyword Magic Tool will suggest long-tail keywords based on your primary keyword:

Save the keywords you want to work with to the Keyword Manager by clicking the gray + next to the keyword. The tool will prompt you to add these keywords to an existing or new list:

Once you’ve got your keywords in a Keyword Manager list, you’ll be able to track the metrics of each keyword:

Click on any keywords to view that keyword in the Keyword Overview tool. Use this tool to view each keyword’s metrics in an easy-to-follow format:

Here, you’ll see a Keyword Variations box, perfect for building out your keyword list.
You’ll also see the questions and related keywords widgets.

Use these to generate further ideas that can help you generate even more long-tail terms.
3. Choose Your First 5-10 Keywords
So at this point, you have a bunch of keywords in your keyword manager.

What’s next?
It’s time to choose the keywords you’ll create pages around.
There are two main factors to use when deciding on a keyword: monthly search volume and competition.

For example, you can see that the term “dog food” gets 110,000 searches per month, which is a lot.

But the KD % is 93%.
Which is super high. This means your site is unlikely to rank for this term anytime soon.
So if your site is new, you want to focus on keywords with low KD % (ideally, less than 20%.)
So in our dog food example, this keyword may be a good fit:

It doesn’t get that many searches (only 110 per month). But the KD is only 18%, which means that you’ve got a shot at ranking for it.
Choosing keywords is definitely more art than science. In general, you want to target low competition terms at first (even if they don’t have a lot of search volume.)
You can always scale up to more competitive keywords as your site’s SEO improves.
Content
A famous saying in SEO goes, “Content is king.” And in 2022, it’s more true than ever. So let’s cover exactly how to create SEO-friendly content.
Understand What Searchers Want to See for a Query
The first step to creating SEO-friendly content is figuring out the search intent for that keyword.
What is search intent, exactly?
Search intent is the underlying reason why someone searched for a given keyword.
For example, take the keyword “organic dog treats.”
Do they want to buy something (commercial intent)? Are they looking for information on TK (informational intent)? Or maybe they’re looking to go to organicdogtreats.com (navigational intent).
Why is this important?
Google can figure out whether or not your site is satisfying search intent.
If so, you’ll get a rankings boost. If not, you’ll have a hard time ranking on Google’s first page.
So before writing a single word, you need to know whether a searcher intends to see informative and educational content or commercial (products, categories, or service) pages.
There are a couple of ways you can do this:
The first is the most time-consuming: head to the SERPs and analyze the pages that rank in the top 10 positions.
Doing this also helps you understand what people searching for that term actually want.
You can also use Semrush’s “Intent” metric to help you determine the intent for that term automatically.
You can see this metric in the Keyword Overview tool:

Intent gives you a quick snapshot of what kind of keywords you are dealing with.
You can learn more about how to identify search intent in this guide.
Create Content that Matches Intent
Your next step is to publish content that matches the search intent you just identified.
So if you found that your keyword had commercial intent, then you want to create a landing page.
If search intent was informational, then you should work on a blog post.
This will ensure that your content at least meets the basic needs of search intent.
If you want to go a bit deeper, you can scan the top 10 results in Google to see exactly what searchers want to see for that keyword.

Specifically, look for things like:
- How long is the content on the first page?
- How is the content structured?
- Are there mostly product and category pages? Or product reviews?
- Are the blog posts written casually or at a professional level?
- What subtopics do the pages tend to cover?
For example, when you read through the first page results for “organic dog treats,” you’ll notice that many of the top-ranking pages are review pages.

Although a few are ecommerce category pages:

(This is known as “mixed intent.” Which is common. It’s not always where 100% of the people searching for a given keyword want the same thing).
But considering that most of the results are product review pages, that’s the type of page you’d want to create.
I’d also take a look at the content itself to get a feel for word count, readability, layout, and more.

Either way, it’s helpful to review the content that’s there. And try to emulate the first page results as much as possible.
(After all, it’s obviously working!)
And if you really want to make sure that your content matches search intent, you can use the Semrush SEO Content Template to help you produce a plan and framework for each page.
Simply enter the keyword you’re primarily targeting with a page, and it will analyze the top 10 results for this keyword and return a templated framework that you can use to build out the content for your page.

You’ll be able to get an insight into the recommended text length, semantically related words to build in, recommended sources of backlinks, and more.
Combine this with the insights you gained from manually analyzing the top 10 results, and you’ll be set to focus on creating content that’s primed to rank on the first page of Google.
Optimize Your Above the Fold Section
The “Above the Fold” section refers to the first thing a user sees when clicking on your webpage.
This is an important section because it’s your website’s “first impression.”
If users see content that indicates they’re in the right place, they’re likely to scroll down.
User Experience
User experience (UX) refers to the overall experience of a searcher/user exploring your website.
UX has a direct and indirect impact on SEO.
UX can directly impact your SEO as a bad UX can mean that Google users spend less time on your site. And bounce from your site quickly.

Both of which suggest to Google that your site isn’t worthy of the first page.
The opposite is also true: a site with a solid UX sends signals to Google that you’re making searchers happy.
UX can indirectly affect SEO because a great UX shows others that your site is a helpful resource, leading to more backlinks coming your way.
For example, one of the reasons that personal finance giant NerdWallet picked up so many backlinks in the early days was its trustworthy design and excellent UX.

Use Enticing CTAs
Great Call-to-Action (CTA) buttons draw the user in without being intrusive or gimmicky.
For example, this CTA appears at the end of one of our articles.

As you can see, this CTA flows naturally with the page and actually provides value for a user that’s wondering what to do next.
Avoid Walls of Text
When you’re writing and optimizing your content, it’s important to consider the white space on your web pages.
Frequent paragraph breaks give readers a visual respite from text walls, making your content easier to read and skim.
For example, this post uses short paragraphs. Which makes it very “skimmable.”

Use Listicles, Bullets, and Numbered Lists
In addition to using white space as a visual respite for users, you can also break content out into bulleted and numbered lists.
Here’s an example from our blog:

Lists Help Users
Lists aren’t a direct ranking factor. But number and bulleted lists tend to have a better chance at securing a featured snippet like the one below.

On-Page SEO
So now you have a piece of high-quality content that’s easy for users to read and skim.
Now it’s time to optimize that page around a keyword (also known as “on-page SEO”).
Here are a few critical on-page SEO techniques that you definitely want to implement on each page of your website:
Optimizing Your Title Tags
Title tags appear as the title of your SERP listing. And are a key ranking factor.

At the most basic level, you’ll want to make sure that the title tags of your site’s pages include the main target keyword for the page (and variants where possible).
But there’s more to optimizing these than simply adding keywords. Our guide on how to write title tags outlines a few other tips to keep in mind as you write your title tags:
- Keep titles about 55-60 characters long
- Use words like HOW, WHY, WHAT, and WHERE—these help people understand what they will find on the page
- Use words like BEST, REVIEW, and ULTIMATE to entice users to click
- Write unique titles for each page
- Keep it simple
Optimizing Your Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are the text that displays under the page title on SERPs.

These are excellent opportunities to encourage users to click on your listing over your competitors’ listings.
Meta descriptions are no longer a direct ranking factor. But a compelling description can positively impact CTR (click-through rate), which is crucial. In our guide to meta descriptions, we recommended the following tips to optimize them properly:
- Keep them about 1-2 sentences (140-160 characters) long
- Don’t forget to include your keyword
- Add a call-to-action if it’s relevant
- Avoid duplicate meta descriptions
- Make them meaningful and descriptive, matching your content
- Target an emotion
Optimizing Your Heading Tags
Another key on-page SEO factor are heading tags, also referred to as H1–H6 tags.
These are used to break up your content into sections like this:

In addition to using subheadings to organize your content, you also want to include your target keywords and related terms inside of each subheading.

Optimizing Your Page URL
Your URL should describe your page’s content concisely.
Think about it this way ...
If you had two page URLs:
- /page-1/
- /red-shoes/
Which one would you say is better optimized?
The second, of course, is for the simple reason that it’s descriptive. By looking at the URL, you can identify that the page is about red shoes.
As a general rule of thumb, URLs:
- Should be descriptive and include the page’s primary keyword
- Use hyphens rather than underscores between words
- Use lower-case, rather than mixing in capital letters
- Be as short as possible while still describing the content of the page
Optimizing Your Images
“Optimizing your images” refers to two different things:
- Optimizing them for SEO
- Making sure they’re optimized to load quickly on any device
Our guide to image optimization offers a few tips to help you get started:
- Name your images correctly to be descriptive.
- Resize images to the dimensions they’ll appear as.
- Reduce file sizes and compress images.
- Optimize alt tags with descriptive text.
Adding Links from Other Pages on Your Site
No guide to SEO basics would be complete without at least touching on internal linking. Linking between pages on your site will:
- Help search engines understand your site’s structure
- Pass authority between pages
- Help users navigate between pages
You can use the Semrush Site Audit tool to help build an ideal internal linking structure.


Use this report to uncover opportunities where you use internal linking to improve your Google rankings.
You can learn more about this process in our guide to internal links.
Link Building
Another central pillar of SEO success comes from building your site’s authority in the eyes of Google.
How do you do that? Backlinks.
In short, a backlink is one website giving a link “back” to your website—essentially giving you a vote of confidence and supporting you. As long as the site linking back to yours is a relevant site, that link can help your site rank higher on Google.
Our post “Link Building for SEO: The Beginner’s Guide” covers 20+ strategies you can try. But let’s review some of the most accessible link-building tactics for SEO beginners.
1. Build Links from Associations, Suppliers, and Connected Business
One of the quickest wins for building links is reaching out to real-life connections your business has.
These connections include:
- Your suppliers
- Associations that you’re a member of
- Your office block’s website
- Your local chamber of commerce
Here’s an example:

Often, all you need to do is reach out to your contact at that site. And they’ll be happy to add your link.
2. Submit Your Site to Quality Directories
If you’re a local business or work in a specific niche, you’ll likely find that there are directories in your space. This can be a speedy way to build a few solid links for your site.
Note that these aren’t old-school directories like DMOZ. Instead, we’re talking about niche directories like this:

Or directories for a specific product type, like this email newsletter directory:

3. Use Haro to Earn Links from the Press
HARO is a platform that connects journalists with business owners and marketers just like you.
Three times a day, Monday to Friday, HARO sends out an email that includes requests from journalists like this:

If there’s a relevant request that makes sense for your business, go ahead and do it. This is an excellent intro to building authority links from news sites and monitoring these emails every day should see opportunities pop up weekly for most businesses. HARO can be very hit or miss. But even a single link from a relevant site can make a difference in your Google rankings (especially if your site is brand new).
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is all about making sure that your site can be crawled and indexed. If search engines can’t crawl or index your site, it will struggle to rank.
Here’s how you can get started:
Setup Google Search Console
If you have not done so already, connect your site to Google Search Console. This free tool helps you identify any problems Google might have when indexing or crawling your site.
Check that Your Site Can Be Indexed and Find Issues
The first thing you’ll want to do with Search Console is double-check that there aren’t any issues preventing key pages from being crawled and indexed.
You can do this with the “coverage” report. Select the report from the left-hand sidebar menu:

Tip: Pay particular attention here to the “excluded” pages. These are where you’ll see specific issues relating to the status of your site’s pages.

You can learn more about understanding the coverage report here.
Additionally, you can inspect any URL on the site (using the URL bar at the top of the page) and see the index status of that page.

Check Your Robot.txt Files
Depending on your site’s CMS, you may have a robots.txt file set up. It’s typically found at: https://www.yourdomain.com/robots.txt
And it should look something like this:

If you don’t have one, you’ll want to create one.
But what is Robots.txt for, exactly?
Robots.txt instructs Googlebot (and other bots) on how to crawl your site. If you’re preventing key site pages from being crawled, address them quickly—this can cause indexation issues.
Similarly, if there are pages that search engine bots shouldn’t crawl that aren’t blocked, this can result in too many pages (either duplicates or low value) being indexed.
You can learn more about robots.txt files here.
Optimize Your Site Speed
No one wants to browse a slow website. That includes both users and search engines.
A slow site speed can negatively impact your SEO performance with a higher bounce rate, poor dwell time, and lower conversion rate.
Also, site speed is a direct ranking factor that Google uses in their algorithm.

Your first step is to benchmark your site’s speed. That way, you’ll know exactly what needs to be fixed (if anything).
Head to your Semrush Site Audit tool dashboard and select the “Issues” tab. Here you’ll see any pages that have been flagged for slow page speed:

From here, it is crucial to understand the specific issues causing slow page speed and the opportunities to make improvements.
You can start by running your site through Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool, where you’ll get recommendations to reduce your load time.

You can learn more about how to improve your PageSpeed Insights score here.
Setup HTTPS
HTTPS has been a ranking factor since 2014.
Yet there are still sites that aren’t secure and still sit on an HTTP domain. Run a check on whether you can access your site using https:// rather than http://.
If you are, then great! There’s no further action needed. If you find that your site still sits on HTTP, speak with your developer and carefully plan a migration to HTTPS or follow this guide.
Mobile SEO
Google uses page speed on mobile as a key ranking metric. They also use mobile-first indexing (in other words, the mobile version of your site is the “main” version in Google’s eyes).
So it’s safe to say that optimizing for mobile is an important part of technical SEO.
You can use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to see how your website appears to mobile users. And if there are any issues that mobile users may have using your website.

Here are a few basic guidelines for making your website mobile-friendly:
- Make sure to use a mobile-friendly website architecture, like a responsive website (meaning the experience is the same across all platforms) or a dynamic website (meaning that the experience is tailored specifically to the platform being used for browsing)
- Don’t let your navigation bar get too cluttered or too long, as this will be harder for mobile users to sort through
- Use animations sparingly as these can slow down mobile page speed
Measuring SEO Success
Now that you’re putting this SEO beginner’s guide into practice, it’s time to track your results.
But how do you go about measuring SEO success? It’s as simple as tracking a few key metrics regularly.
Organic Traffic
Organic traffic refers to the number of visitors to your site from Google’s organic results.
The best way to measure organic traffic is using Google Analytics (GA).

(Haven’t set up GA yet? No worries, we have a 5-step guide on how to get all set up)
If your organic traffic numbers are going up, that’s a good indicator that your content resonates with people, your keywords aren’t too competitive, and the links you’re building are working.
If your traffic numbers are trending down, your site may be running into technical SEO issues, targeting overly-competitive keywords, or your site just needs more time to start seeing SEO results.
Average Session Duration and Bounce Rate
Average session duration and bounce rate are two metrics that help determine if your content resonates with your audience. You can find both of these metrics in Google Analytics.
Average session duration measures the time between two clicks: the first click that brought a user to your page and the second click that takes them elsewhere.

“Elsewhere” can be another page on your website, back to the SERPs… or any other page.
Avg. session duration can tell you a lot about the performance of your content.
If users aren’t finding answers to their queries, or if your content is boring, chances are that a user will click away to another site.
Bounce rate describes just how many single-page sessions your page had—that is, how many people came to one page on your site and left immediately after.

A high bounce rate can indicate that your content isn’t well-aligned with users’ search queries. You may have to do further keyword research or streamline your content to serve your site visitors better.
Conversion Rate
A conversion is defined as the number (or percentage) of users who perform your website’s desired action. Desired actions in this context could be submitting their email address and contact information or purchasing a product page.
To calculate your conversion rate, divide the number of conversions by the number of visitors to your site. Once you have this number, multiply by 100. This will give you a percentage.
You can get the number of unique visitors to a site by entering the domain into our Traffic Analytics tool.

Determining your desired action/conversion will depend on your business goals. It can be as simple as setting a plan for a certain number of page visits to your contact page or something more extensive like making a purchase.
If your SEO is successful, you’ll hopefully see more organic traffic. If you’re noticing that you’re failing to convert users into leads and buyers, you’ll want to determine if:
- Your desired conversion is something reasonable (like a new visitor signing up for a newsletter)
- You’re targeting keywords that your target customers use to find info in Google
- Your site has a UX that encourages people to stay on your site
Final Thoughts
First, congratulations on taking your first steps into the world of SEO!
SEO is one of the most powerful digital marketing channels out there. Where else can you get a steady stream of targeted traffic coming to your site?
What's Your Reaction?











































































